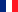
Our bi-arm platform
Our bi-arm platform is composed of two Kuka LWR arms, a Shadow hand equiped with five Biotac tactile sensors, a Barrett hand, force sensors, a pan-tilt-zoom stereo-camera head and RGBD-cameras.
Visual servoing of the bi-arm platform
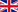
Our bi-arm platform is composed of two Kuka LWR arms, a Shadow hand equiped with five Biotac tactile sensors, a Barrett hand, force sensors, a pan-tilt-zoom stereo-camera head and RGBD-cameras.
UGV/UAV Visual Control
The first video illustrates a realistic simulation example where twelve Pioneer 3-AT mobile robots are driven to a circular desired configuration using three camera-equipped UAVs. The video is divided into four windows, which show: a general view of the system (top-left), a subjective view focused on one UAV (top-right), a subjective view focused on one mobile robot (bottom-left), and the sequence of images captured by one of the UAV-mounted cameras (bottom-right).
UGV/UAV Visual Control
The second video illustrates an experiment with four Khepera III robots, which are driven to a square-shaped desired configuration using the images captured by two cameras. One of them is fixed over the workspace, while the other is manually handled and moves throughout the experiment. The video is divided into three windows, which show: the sequence of images captured by the moving camera (top-left), the sequence of images captured by the fixed camera (bottom-left), and the motion of the robots registered by an external video camera (right).
Visual Control by pushing
By pushing, the two arms are visually controlled.
Visual Control by pushing
Using visual servoing, objects can also be pushed with mobile robots.
Robotized meat cutting
We developed with our partners of the SRDViand project a robotic platform for automatic meat cutting. The cutting trajectory is computed using active vision and it is tracked with vision/force based control strategies.
Vision-based Autonomous control of an electrical vehicle
The Electrical vehicle is controlled using visual information provided by a fish-eye camera. The visual memory concept is exploited to localize the vehicle.
UGV/UAV Visual Control
The UGVs are controlled using visual features provided by the UAVs.